6.8 KiB
Instructions for setting up the .NET Core debugger
This page gives you detailed instructions on how to debug code running under .NET Core in VS Code.
Your Feedback
File bugs and feature requests here and join our insiders group to help us build great tooling for .NET Core.
First Time setup
1: Get Visual Studio Code
Install Visual Studio Code (VSC). Pick the latest VSC version from here: https://code.visualstudio.com Make sure it is at least 1.5.
If you are not sure what version you have, you can see your version of VS Code:
- OSX: Code->About Visual Studio Code
- Windows / Linux: Help->About
2: Install .NET command line tools
Install the .NET Core command line tools (CLI) by following the installation part of the instructions here: https://www.microsoft.com/net/core
OSX: .NET Core requires openSSL to work. Don't forget this! Execute: brew install openssl
3: Install C# Extension for VS Code
Open the command palette in VS Code (press F1) and type ext install C# to trigger the installation of the extension. VS Code will show a message that the extension has been installed and it will restart.
If you have previously installed the C# extension, make sure that you have a recent version. You can check this by opening the command palette (press F1) and running Extensions: Show Installed Extensions.
4: Wait for download of platform-specific files
The first time that C# code is opened in VS Code, the extension will download the platform-specific files needed for debugging and editing. Debugging and editor features will not work until these steps finish.
Once for each project
The following steps have to executed for every project.
1: Get a project
You can start from scratch by creating an empty project with dotnet new. Begin by opening the terminal in Visual Studio Code (View->Integrated Terminal) and type these commands:
cd ~
mkdir MyApplication
cd MyApplication
dotnet new
dotnet restore
If you want a web project (ASP.NET project) use dotnet new -t web. For web projects, makes sure to run bower install before running so that they can restore assets.
2: Open the directory in VS Code
Go to File->Open and open the directory in Visual Studio Code. If this is the first time that the C# extension has been activated, it will now download additional platform-specific dependencies.
3: Add VS Code configuration files to the workspace
VS Code needs to be configured so it understands how to build your project and debug it. For this there are two files which need to be added -- .vscode/tasks.json and .vscode/launch.json.
- Tasks.json is used to configure what command line command is executed to build your project, and launch.json configures the type of debugger you want to use, and what program should be run under that debugger.
- Launch.json configures VS Code to run the build task from tasks.json so that your program is automatically up-to-date each time you go to debug it.
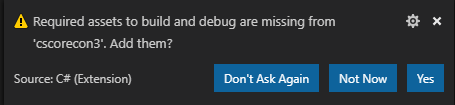
If you open the folder containing your project.json, the C# extension can automatically generate these files for you if you have a basic project. When you open a project and the C# extension is installed, you should see the following prompt in VS Code:
Clicking Yes on this prompt should add these resources.
Creating configuration files manually
If your code has multiple projects or you would rather generate these files by hand, here is how --
.vscode/tasks.json: Start with this example which configures VS Code to launch dotnet build. Update the cwd property if your project isn't in the root of the open folder. If you don't want to build from VS Code at all, you can skip this file. If you do this, you will need to comment out the preLaunchTask from .vscode/launch.json when you create it.
.vscode/launch.json: When you want to start debugging, press the debugger play button (or press F5) as you would normally do. VS Code will provide a list of templates to select from. Pick ".NET Core" from this list and the edit the program property to indicate the path to the application dll or .NET Core host executable to launch. For example:
"configurations": [
{
...
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/MyLaunchingProject/bin/Debug/netcoreapp1.0/MyLaunchingProject.dll",
4: Start debugging
Your project is now all set. Set a breakpoint or two where you want to stop, click the debugger play button (or press F5) and you are off.
Debugging Code compiled on another computer
If your code was built on a different computer from where you would like to run in there are a few things to keep in mind --
- Source Maps: Unless your local source code is at exactly the same path as where the code was originally built you will need to add a sourceFileMap to launch.json.
- Portable PDBs: If the code was built on Windows, it might have been built using Windows PDBs instead of portable PDBs, but the C# extension only supports portable PDBs. See the portable PDB documentation for more information.
- Debug vs. Release: It is much easier to debug code which has been compiled in the
Debugconfiguration. So unless the issue you are looking at only reproduces with optimizations, it is much better to use Debug bits. If you do need to debug optimized code, you will need to disable justMyCode in launch.json.
Configurating launch.json for C# Debugging
Attach Support
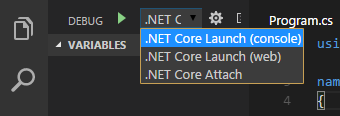
The C# debugger supports attaching to processes. To do this, switch to the Debug tab, and open the configuration drop down.
Select the '.NET Core Attach' configuration. Clicking the play button (or pressing F5) will then try to attach. In launch.json, if processId is set to "${command:pickProcess}" this will provide UI to select which process to attach to.
Remote Debugging
The debugger supports remotely launching or attaching to processes. See Attaching to remote processes in the wiki for more information.